- +91 9321330888
- info@crystapeaksolutions.com
- Sr.No. 201, Hiss.No. 1159, SADESATRA NALI, HADAPSAR, PUNE 411028 MAHARASHTRA
Basic XRPD Data Analysis (determine diffraction peak position, intensity )
Identification & Quantification of Crystalline Phases
Calculating lattice parameters and crystallite size
Calculating FWHM, Signal to noise ratio, etc.
Determination of the % Crystallinity
Reports in the form of PDF file/excel data file/ASCII DAT file
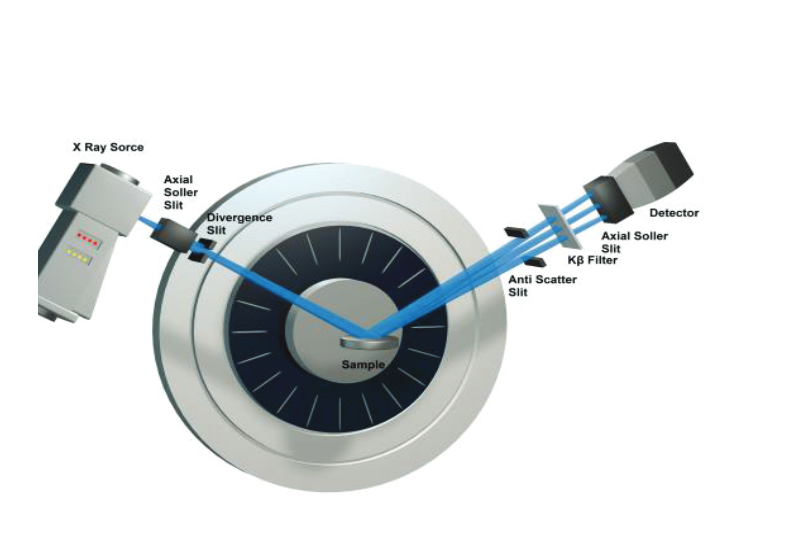
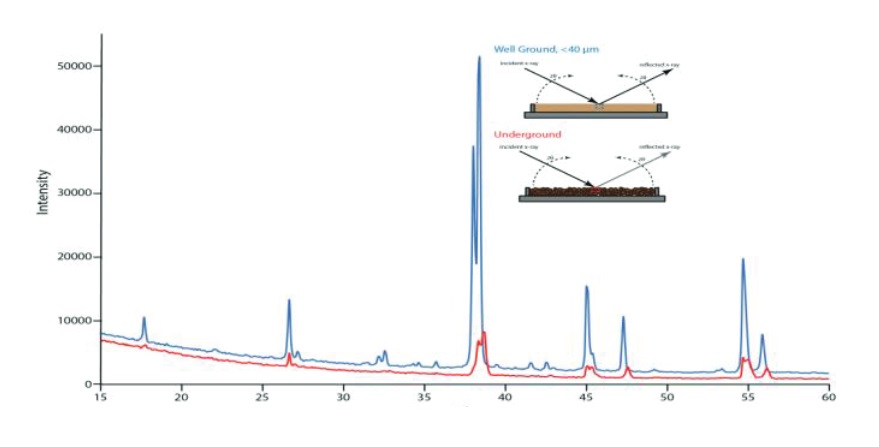
X-Ray Diffraction analysis (XRD) is a characterization technique used for crystalline materials. X-ray diffraction patterns are unique to the periodic atomic arrangements in a specimen and are widely used for phase identification. In a diffractometer, incident X-rays are scattered (diffracted) at specific angles from the sample’s lattice planes, resulting in diffraction peaks characteristic of simple’s crystal structure. The diffraction patterns give information like phase, atomic plane spacing (d-spacing), crystal structure, crystallinity, strain, crystallite size, crystal defects, etc.
The quantity of sample required depends on the type of analysis to be performed. If only a simple XRD Diffractogram is needed it can be done with as little as 1gm of powder sample with or even less depending on the nature of the material.
The ideal average particle size of the XRD is 10~50um (Particle size is inversely related to both the degree of randomness of the crystallites and the measured intensity).